
12 May Interview with the ARACOWELD experiment
The KYKLOS4.0 Open Call #2 is funding seventeen experiments that are developing technological solutions of value for the manufacturing domain.
The project will be releasing a series of interviews over the course of the coming weeks with the objective of promoting the work being implemented in these experiments and allowing our readers to understand potential uptake of the solutions being developed by them.
This is the second of the seventeen interviews with the experiments funded under the open call. Today, we interview the ARACOWELD experiment.
* * * * *
Explain your project in one sentence.
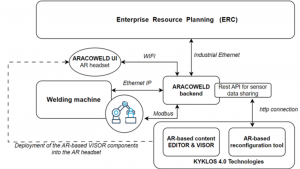
ARACOWELD stands for “augmented reality for agile collaborative welding”. More specifically ARACOWELD uses augmented reality technology to allow features such as contextual or on-the-spot training, real-time operator machine/process monitoring, and simple operator task confirmations and malfunction reporting in the context of welding using collaborative robots.
How is KYKLOS4.0 project and the selected services (and components) bringing value to your project?
We are making extensive and comprehensive use of the KYKLOS 4.0 augmented reality services for our project, taking full advantage of the remarkable features and functionalities they offer. In particular, we are utilising the “AR-based content editor” for the creation of step-by-step operative workflows, ensuring the complete training of the operator to proficiently perform a task. Moreover, we are also using the “AR-based reconfiguration tool” to implement a virtual panel, enabling seamless monitoring of the welding process. It is important to mention that the user experience provided by KYKLOS 4.0 services is exceptional and highly intuitive. This results in a smooth and efficient interaction between the operator and the AR technology, further enhancing the overall effectiveness of our project. Furthermore, the integration with various AR devices is seamless and hassle-free, allowing for a wide range of compatibility and accessibility, which only adds to the outstanding performance of the KYKLOS 4.0 services. Given all these factors, it is abundantly clear that the KYKLOS 4.0 services are playing a central and instrumental role in the successful execution of our project while delivering a good user experience and seamless integration with our AR device.
How is your solution contributing to circular manufacturing?
The ARACOWELD experiment leverages augmented reality (AR) technology to improve the efficiency and effectiveness of collaborative welding processes. By doing so, it plays a significant role in promoting the circular economy. Here are some ways the ARACOWELD experiment contributes to the circular economy:
- Enhanced training and skill development: AR technology accelerates the learning curve for new welders, enabling them to quickly acquire essential skills. This leads to higher-quality work with fewer errors, which in turn reduces the need for rework and material waste.
- Improved welding accuracy: The AR technology in ARACOWELD ensures greater precision and accuracy in the welding process, reducing the likelihood of defects and the need for post-welding repairs. This contributes to a reduction in waste materials and energy consumption.
- Reduction in material overuse: ARACOWELD’s AR system enables welders to use the exact amount of welding consumables needed for each task, preventing overuse of materials and reducing overall consumption.
- Extended product lifecycle: As ARACOWELD improves welding quality, it enhances the durability and longevity of the end products. This results in a reduced need for frequent repairs or replacements, ultimately decreasing the demand for raw materials and promoting the circular economy.
In conclusion, the ARACOWELD experiment’s incorporation of augmented reality into the welding process supports the circular economy by reducing waste, optimising resource usage, and promoting efficient collaboration. This innovative approach not only leads to cost savings but also supports environmental sustainability.
How will your solution be replicated and used in other manufacturing environments?
The ARACOWELD solution, with its hardware and software architecture, can serve as a building block for adaptation in various manufacturing environments that require real-time monitoring and step-by-step training. By leveraging augmented reality (AR) technology and tailoring the hardware and software components to specific industry needs, ARACOWELD can contribute to improved efficiency, reduced waste, and enhanced collaboration. Here are some examples of industries in which it could be applied:
- Automotive Manufacturing: ARACOWELD’s AR technology can be used for real-time monitoring and guidance in tasks such as assembly, painting, and quality control, ensuring optimal use of resources and reducing errors.
- Aerospace Industry: Complex assembly processes, component installation, and quality assurance tasks in the aerospace industry can benefit from ARACOWELD’s AR capabilities, leading to faster production times and increased accuracy.
- Food and Beverage Processing: ARACOWELD can be adapted to ensure proper handling, preparation, and packaging processes in food and beverage manufacturing, reducing waste and ensuring compliance with hygiene and safety standards.
- Pharmaceutical Manufacturing: The AR solution can be tailored to support pharmaceutical production processes, including mixing, compounding, and quality assurance, ensuring product safety and reducing contamination risks.
- Textile Manufacturing: In textile production, ARACOWELD can provide guidance on weaving, dyeing, and finishing processes, ensuring optimal use of resources and reduced waste generation.
By adapting the hardware and software architecture of the ARACOWELD solution to the specific requirements of these industries, real-time monitoring and step-by-step training can significantly improve overall efficiency and promote sustainable manufacturing practices.
What advice would you give to companies wishing to make their manufacturing processes more circular?
Companies seeking to make their manufacturing processes more circular can adopt various innovative and forward-thinking strategies to create sustainable and efficient operations. Here are some suggestions that we would make:
- Leverage digital technologies: Utilise cutting-edge digital tools, such as augmented reality (AR), digital twins, artificial intelligence (AI), and the Internet of Things (IoT), to enhance resource management, optimise processes, and reduce waste.
- Modular design and standardisation: Design products with modularity and standardisation in mind to facilitate repair, refurbishment, and remanufacturing, thereby extending product lifecycles and reducing the need for raw materials.
- Waste as a resource: View waste as a potential resource and explore opportunities to upcycle, recycle, or repurpose waste materials within the production process or for other applications.
- Invest in employee training and education: Encourage a circular economy mindset among employees by providing training and education on sustainability, waste reduction, and resource optimisation.
- Design for disassembly: Develop products that can be easily disassembled at the end of their lifecycle, simplifying recycling and component recovery processes.
- Implement eco-friendly packaging: Use sustainable, biodegradable, or reusable packaging materials to minimise packaging waste and reduce the environmental impact.
- Continuous improvement mindset: Embrace a culture of continuous improvement, regularly evaluating and refining processes to identify new circular economy opportunities and potential areas for optimisation.
By adopting these approaches, companies can transform their manufacturing processes to become more circular, contribute to environmental sustainability, and create long-term value for business and stakeholders
* * * * *
About the ARACOWELD project
The ARACOWELD project – Augmented reality for agile collaborative welding – is implemented by two partners: Canonical Robots S.L. (Spain), Oxiplant (Spain).
Summary: The main objective of the project is to provide modern capabilities to an automatic welding system to improve the human-machine interaction and contribute to the circular economy.

